Applied Design Patterns with Java
Behavioral :: Visitor (331) {C ch 26}
Applicability
Use the Visitor pattern when:
- an object structure contains many classes of objects
with differing interfaces, and there is a need to perform operations on these objects that depend on their concrete
classes.
- many distinct and unrelated operations need to be performed
on objects in an object structure, and it is desirable to avoid "polluting" their classes with these
operations. Visitor allows keeping related operations together by defining them in one class. When the object
structure is shared by many applications, use Visitor to put operations in just those applications that need them.
- the classes defining the object structure rarely change,
but there is often a need to define new operations over the structure. Changing the object structure classes requires
redefining the interface to all Visitors, which is potentially costly. If the object structure classes
change often, then it's probably better to define the operations in those classes.
Structure
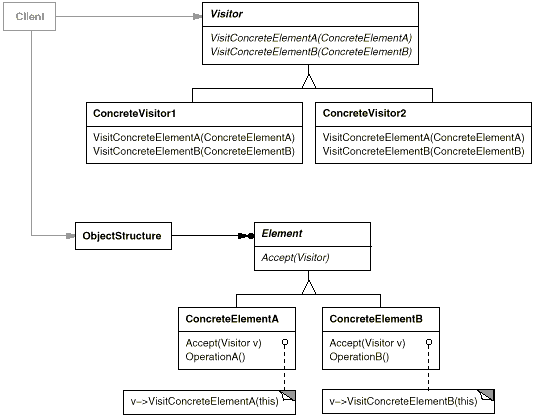
Participants
- Visitor
(NodeVisitor) declares a Visit operation for each
class of ConcreteElement in the object structure. The operation's name and signature identifies the class that
sends the Visit request to the Visitor. That lets the Visitor determine the concrete class of the element being visited. Then
the Visitor can access the element directly through its particular interface.
- ConcreteVisitor (TypeCheckingVisitor) implements each operation declared by Visitor. Each operation
implements a fragment of the algorithm defined for the corresponding class of object in the structure. ConcreteVisitor
provides the context for the algorithm and stores its local state. This state often accumulates results during
the traversal of the structure.
- Element (Node)
defines an Accept operation that takes a visitor as an argument.
- ConcreteElement
(AssignmentNode,VariableRefNode) implements an Accept operation that takes a Visitor as an argument.
- ObjectStructure
(Program) can enumerate its elements, it may provide a high-level interface to allow the Visitor to visit its
elements, and it may either be a Composite (163) or a collection such as a list or a set.
Catalog Behavioral Prev Next

